Unified Data Foundation for AI & Analytics
1. Challenges from Data Silos
[Placeholder: Slide - Deriving insights from data can be challenging]

Organizations often hit blockers because data is split across isolated silos:
- Data silos: data lakes and data warehouses run independently and are hard to blend.
- People silos: data lives inside different functions with little collaboration.
- Business silos: compliance, cost, and governance constraints slow sharing.
-> Insights get fragmented, innovation slows, and AI adoption stalls.
Data Lake + DW -> Data silo
Data Owners -> People silo
Compliance/Cost -> Business silo
2. Evolution of Data Requirements
[Placeholder: Slide - Ever evolving data requirements]

Traditional
- Focused on structured and semi-structured data.
- Driven by batch pipelines.
- Stored in operational and analytical systems.
- Governance centered on tables, files, and dashboards.
Modern
- Augments structured data with unstructured sources (documents, media, knowledge).
- Vector databases become core for AI workloads.
- Self-service governance: policies extend to AI prompts and responses.
- Stream-first pipelines replace legacy batch to power real-time AI and analytics.
Traditional -> Structured data, batch, centralized governance
Modern -> Vector DB, mixed data, stream-first
-> Data now must be flexible, diverse, and AI-ready.
3. End-to-End Data Strategy
[Placeholder: Slide - End-to-end data strategy]
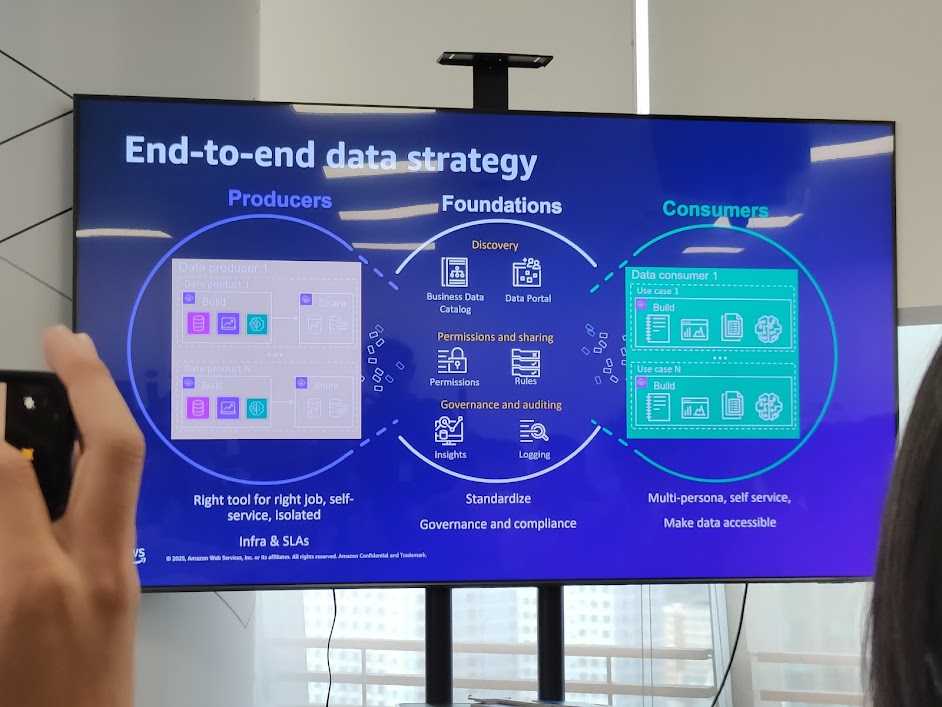
A complete end-to-end data strategy includes:
- Producers: create and share data, choose the right tools, embrace self-service.
- Foundations: standardize governance, auditing, discovery, and permissions.
- Consumers: multi-persona, self-service, easy access across many use cases.
-> Shift the mindset from a single-purpose stack -> a unified shared platform.
[ Producers ] -> [ Foundations ] -> [ Consumers ]
Build/Share Catalog/Govern Use cases, BI, AI
4. Metadata at the Center
[Placeholder: Slide - Metadata centric pipeline]

When metadata sits at the heart of the data ecosystem:
Data sources (structured + unstructured) get standardized and enriched.
Metadata unlocks: find, share, understand, access, act, and monitor.
This powers analytics and AI such as:
- GenAI / RAG.
- Forecasting and classification.
- BI and decision intelligence.
- Graph analytics and anomaly detection.
Data Sources -> Prep/Enrich -> Metadata -> Analytics/AI
-> Metadata is no longer just a catalog; it becomes the orchestration layer for AI and analytics.
5. Relational & Purpose-built Databases
[Placeholder: Slide - Complete set of relational and purpose-built databases]

AWS offers purpose-built databases for every workload:
- Relational: RDS, Aurora (traditional OLTP and OLAP).
- Key-Value: DynamoDB.
- Document: DocumentDB.
- Graph: Neptune.
- Caching: ElastiCache.
- Time-series: Timestream.
- Ledger: QLDB.
- Wide column: Keyspaces.
- Memory: MemoryDB for Redis.
-> Embrace polyglot persistence instead of one-size-fits-all.
6. Why one-size-fits-all does not work
[Placeholder: Slide - Developers want the right datastores]

A single relational database cannot cover every demand:
- Performance issues as datasets grow.
- Lack of scalability for surging workloads.
- Lack of flexibility: developers are boxed in.
- Cannot integrate every data type (images, vectors, graphs, etc.).
-> Developers need datastores matched to the unique traits of each application.
Performance low Scalability low
Flexibility low Integration low
7. Enabling Vector Search
[Placeholder: Slide - Enabling vector search across services]

AWS has woven Vector Search across multiple services:
- OpenSearch Service, OpenSearch Serverless.
- Aurora PostgreSQL, RDS for PostgreSQL.
- DocumentDB, DynamoDB (zero-ETL).
- MemoryDB, Neptune.
-> Vector search is the AI-native infrastructure layer that powers GenAI and RAG.
OpenSearch + AuroraPG + RDS -> Vector Search
DynamoDB + MemoryDB + Neptune -> Vector Search
8. AWS Analytics Stack
[Placeholder: Slide - Comprehensive set of analytics services]

The AWS end-to-end analytics toolkit:
- Amazon Athena: interactive, serverless querying.
- Amazon EMR: large-scale data processing.
- Amazon Kinesis / MSK / Flink: real-time analytics.
- Amazon Redshift: data warehousing with serverless options.
- AWS Glue: data integration and ETL.
- Amazon QuickSight: business intelligence.
- Amazon OpenSearch: operational analytics.
-> Covers the journey from ingest -> transform -> analyze -> visualize.
9. Key Insights for the Notion materials
- Data silos are the top blocker for AI adoption -> build a unified data foundation.
- Metadata plus vector databases unlock GenAI and RAG experiences.
- AWS supplies the full stack: diverse databases + analytics services + governance.
- Organizations should practice polyglot persistence to match datastore to workload.
-> This is how AWS delivers modern data infrastructure for AI and analytics workloads.